University of Arizona – Lead Investigator Dr. James Bibb
NOVEL MECHANISMS and THERAPEUTICS FOR SDHB MUTATION-DRIVEN PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA
Genetically determined metabolic dysfunctions or inborn errors of metabolism disrupt normal resting or senescent state bioenergetic sensing, causing cells to undergo uncontrolled proliferation. Such genetic disorders are typified by loss-of-function mutations in succinate dehydrogenase (SDH), which both impairs metabolism and causes uncontrollable cell proliferation in adrenal and paraganglia glands resulting in two related recalcitrant, debilitating, and lethal cancers, pheochromocytoma (PC) and paraganglioma (PG).
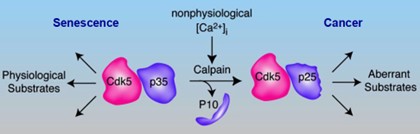
How these mutations cause these cancers has been poorly understood. Thanks to SDHB PheoPara Coalition grant support, in 2022 we reported a new pathway by which deficiencies in SDHB mutations that cause buildup of the metabolic intermediate succinate, hyperactivates succinate receptors, resulting in loss of adrenal chromaffin cell calcium homeostasis. This activates the protease, calpain, to cleave the protein p35 which serves as the activating cofactor of a protein kinase named Cdk5. Conversion of Cdk5/p35 to Cdk5/p25 renders the kinase aberrantly active and has the downstream effect of inactivating a critical bioenergetic sensor, AMP-kinase. This releases cells from the resting state and they uncontrollably divide and multiply. Thus, we discovered an important mechanistic signaling cascade by which SDHB mutations give rise to PC. We also introduced the first inducible/arrestable clinically accurate animal model of PC, and demonstrated a newly discovered anti-Cdk5 drug, MRT3-007 which halted or regressed PC tumors across several preclinical models.
These advances underline the importance of continuing this research in two critical directions. First, it is now clear that Cdk5 is a principal drug discovery target for PC treatment. Second, better mechanistic understanding of how aberrant Cdk5 causes SDHB mutation-linked PC/PG will reveal additional specific targets for therapy development. With SDHB PheoPara Coalition support, we are aggressively pursuing these two goals. We aim to bring biomarker guided patient specific precision medicine cures for PC and PG. We are aggressively leveraging the innovative systems and tools we have developed to better understand the disease mechanisms and uncover new targets for treatment.
Like all kinases, Cdk5 catalyzes protein phosphorylation, transferring a phosphate from ATP to specific sites on proteins. Our current anti-Cdk5 drugs act at the enzyme’s ATP binding site and show efficacy in animal models of PC, as proof of principle. However, they are not adequately specific and exhibit toxicity at doses 4-fold higher than those found to be minimally effective. To achieve a wider treatment dose window, new drugs with different modes of action are needed. We are now screening a novel peptoid inspired, conformationally constrained oligomer (PICCOs) bead display compound library for compounds that will block Cdk5/p25 activity through allosteric interactions beyond the ATP binding site or through protein-protein interaction disruption. Preliminary studies indicate that this approach is producing hits for compounds that bind tightly to Cdk5/p25. We are refining the screen and hope to have our first validated compounds to begin preclinical testing soon. Effective and safe compounds will be paired with a diagnostic biomarker assay designed to identify Cdk5-driven tumors and thus direct these therapies as a novel precision medicine approach.
Concomitantly, we are aggressively pursuing pathways that are both upstream and downstream of Cdk5/p25 so that new targets may be identified and adapted to drug library screening. Blocking p35 conversion to p25 may be an effective treatment strategy. Thus, we are creating a new system to identify the proteins that interact with p35 (i.e., the p35 tumorigenic ‘interactome’) when succinate receptors are activated. We hypothesize that disruption of key binding partners will prevent efficient calpain cleavage of p35. We also discovered novel pathways by which aberrant Cdk5 activates cancer causing gene expression. These gene regulatory mechanisms are critical for neoplastic programming downstream of Cdk5/p25. Studying these will yield new and specific therapeutic targets. We believe our research will lead to cures for PC and PG. However, this work is challenging, requires resources, and would not be possible without SDHB PheoPara Coalition support. Thank you for your support.